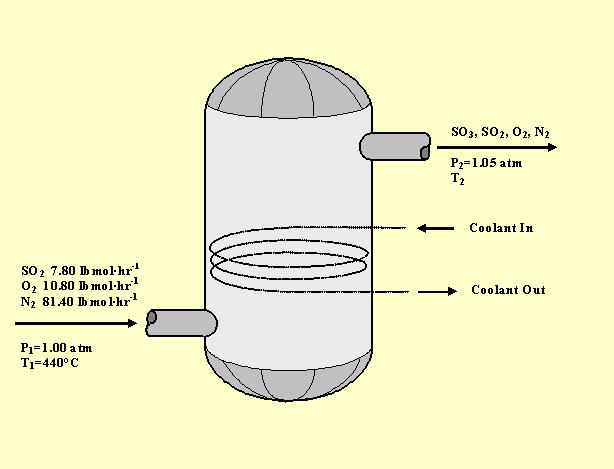
Hot gases from a sulfur burner enter a converter, in which the sulfur dioxide present is to be oxidized catalytically to sulfur trioxide, according to the reaction:
How much heat must be removed from the converter per hour to permit a 95% conversion of the sulfur dioxide for the conditions shown in the figure below? Assume that the converter is large enough for the components of the exit gas to be in thermodynamic equilibrium with one another. That is, the partial pressures of the exit gases are related by the equilibrium constraint:
Where Kp is the equilibrium constant, and the p's are partial pressures.
Approximate values of Kp for this reaction are:
T (K) |
600 |
700 |
800 |
900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Kp (atm^-1/2) |
9500 |
880 |
69.5 |
9.8 |