Lab registration:
If you missed the lab, follow the instruction on the lab web page and register for comp212.
Reading Assignment for this week:
Java Programming Language (JPL): 1.1-1.5, 1.6.1, 1.7.1, 1.7.2, 1.9, 1.10, 2,1-2.8, 2.13, 2.14.
Notes on OO Program Design, by Dr. Cartwright: 1.1, 1.2.1-1.2.5, 1.2.9, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6
Summary of Java Syntax
A Java program consists of one or more classes one of them must be public and must have a method with the following signature:
public static void main (String[] args).
Basically, the main method will instantiate appropriate objects and send them "messages" (by calling their methods) to perform the desired tasks.

Comments syntax:
// Line-oriented.
/*
block-oriented
can span several lines.
*/
Class definition syntax: [�] means optional.
[public] class class-name [inheritance-specification]
{
[field-list;]
[constructor-list;]
[method-list;]
}
Examples:
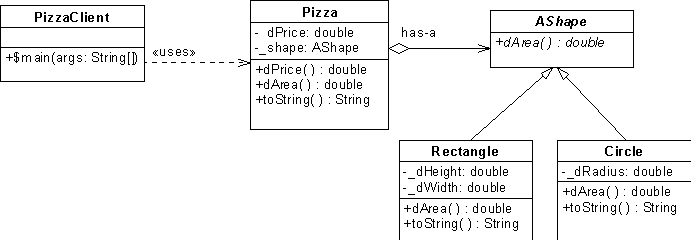
public class PizzaClient
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Pizza cirPizza = new Pizza (4.69, new Circle (2.5)); // instantiation
// and assignment.
System.out.println (cirPizza); // output to standard output stream.
Pizza rectPizza = new Pizza (4.49, new Rectangle (5, 4));
System.out.println (rectPizza);
System.out.print ("Round Pizza is a better deal than Rectangular Pizza: ");
System.out.println ((cirPizza.dPrice () / cirPizza.dArea () < rectPizza.dPrice () / rectPizza.dArea ()));
// NOTE: infix notation for arithmetic expressions, and
// "dot" notation for method calls.
}
}
NOTE: Each Java statement must terminate with a semi-colon.
public class Rectangle extends AShape
{
private double _dHeight; // Note the use of the underscore.
private double _dWidth;
public Rectangle (double dWidth, double dHeight)
{
_dHeight = dHeight; // the underscore helps distinguish the field from the
// parameter.
_dWidth = dWidth;
}
public double dArea()
{
return _dHeight * _dWidth; // infix notation!
}
public String toString ()
{
return "Rectangle (width = " + _dWidth + ", heigth = " + _dHeight + ")";
}
}
Field list syntax: A field list consists of zero or more field declarations of the form
[static] [final] [public | private | protected] field-type field-name [assignment];
Constructor list syntax: A constructor list consists of zero or more constructor definitions of the form
[public | private | protected] class-name ([parameter-list])
{
[statement-list;]
}
NOTE: The constructor's name is the same as the class name. Constructors are used for initialization of the object during the object's instantiation only.
Method list syntax: A method list consists of zero or more method definitions of the form
[static] [final] [public | private | protected] return-type method-name [param-list]
{
[statement-list;]
}
A return type void means the method does not return any value.
Param-list looks like: type1 param1, type2 param2, �, typeN paramN