Heaps and Heap Sort
Heap Sort
-
Heap Sort, like Selection Sort, is a hard-split, easy-join method.
-
Think of Heap Sort as an improved (faster) version of Selection Sort.
-
Specifically, split(), which finds the largest element in the subarray,
is made to run in O(log n) steps instead of O(n) steps, where n is the
subarray length.
-
Since split() is performed n times, where n is the (overall) array length,
Heap Sort takes O(n log n) steps.
How is split() sped up?
-
The elements in the unsorted portion of the array are organized into a
heap.
A heap is a data structure that is optimized for repeatedly finding and
removing the largest (smallest) element.
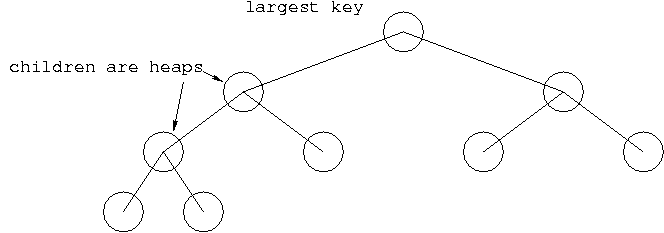
What is a Heap?
-
A heap is a binary tree that (1) is almost perfectly balanced (we allow
a variation of at most 1 in path lengths from the root to the leaves) and
that (2) further exhibits the heap property:
-
the root, if non-null, is the largest (smallest) key in the tree, and its
left and right subtrees are themselves heaps.
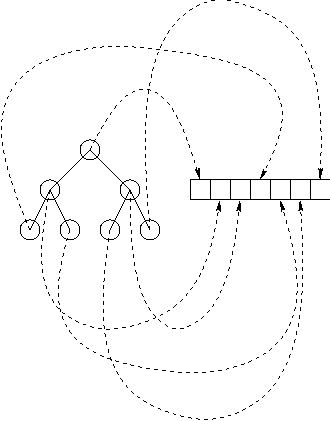
Implementing a Heap?
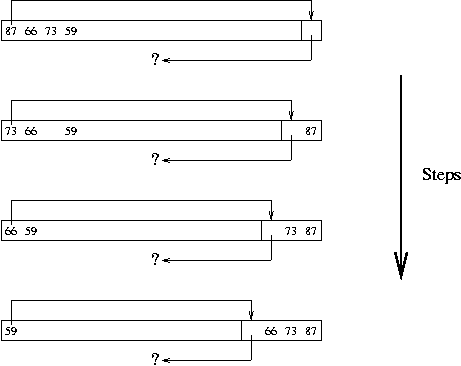
Heap Sort Basics
Heap Sort: split()
public int split(int[] A, int lo, int hi)
{
// Swap A[hi] and A[lo].
int temp = A[hi];
A[hi] = A[lo];
A[lo] = temp;
// Restore the heap property by ``sifting down''
// the element at A[lo].
Heapifier.Singleton.siftDown(A, lo, lo, hi - 1);
return hi;
}
Example of siftDown()
siftDown(): The Implementation
public void siftDown(int[] A, int lo, int cur, int hi)
{
int dat = A[cur];
// hold on to data.
int child = 2 * cur + 1 - lo; // index of left child of
A[cur].
boolean done = hi < child;
while (!done) {
if (child < hi && A[child + 1] <
A[child]) {
child++;
} // child is the index of the smaller of the
two children.
if (A[child] < dat) {
A[cur] = A[child];
cur = child;
child = 2 * cur + 1 - lo;
done = hi < child;
}
// A[cur] is less than its children.
else {
// A[cur] <= A[child].
done = true;
// heap condition is satisfied.
}
// A[cur] is less than its children.
}
// location found for temp.
A[cur] = dat;
}
Initializing the Heap: HeapSorter()
public class HeapSorter extends ASorter
{
public HeapSorter(int[] A, int lo, int hi)
{
for (int cur = (hi - lo + 1) / 2; cur >= lo;
cur--) {
Heapifier.Singleton.siftDown(A,
lo, cur, hi);
}
}
. . .
Summary of Sorting
|
Best-case Cost |
Worst-case Cost |
| Selection |
O(n2) |
O(n2) |
| Insertion |
O(n) |
O(n2) |
| Heap |
O(n log n) |
O(n log n) |
| Merge |
O(n log n) |
O(n log n) |
| Quick |
O(n log n) |
O(n2) |
-
Selection sort performs the least swaps, O(n), in the worst case.
-
Insertion sort is best if the array is nearly or already sorted.
-
Heap sort performs a constant factor more comparisons than Merge sort
-
Merge sort requires extra storage proportional in size to the input.
-
Quick sort typically (expected case) outperforms Heap and Merge sort because
of its simplicity.





