Use of the Palle, Nolan and Miller Correlation found in 2005 Physics
of Fluid Article
The Correlation Takes the Basic Form
D(T,P) = f(Tr,Pr)*(Patm/P) *D(T,Patm)
Maple used to compute Diffusivities
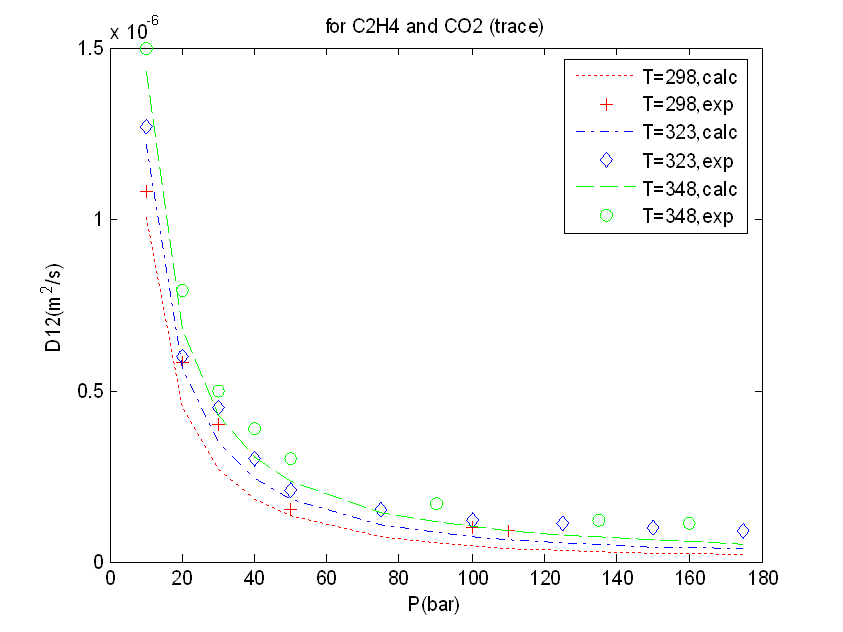
Calculate the diffusivity of C2H4 and trace CO2
> restart
Calculate the Diffusivity at the given temperature and
atmospheric pressure using the start301 program dcalc
> ![]() D12o := array ( 1…3, [1.1361e-5 * m^2/s , 1.3284e-5 * m^2/s,
1.5244e-5 *m^2/s]);
D12o := array ( 1…3, [1.1361e-5 * m^2/s , 1.3284e-5 * m^2/s,
1.5244e-5 *m^2/s]);
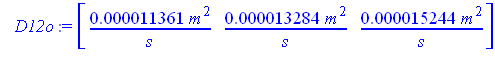
Also obtain critical temperature and critical pressure
from start301.
> Pc1:=5066.3 kPa;Pc2:=7380.5
kPa; Tc1:=282.4 K;Tc2:=304.2 K; kPa:=1/100
bar;
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
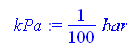
Indicate mass fractions (if unknown, assume equimass)
> ![]()
![]()
![]()
Calculate the mean critical temperature and mean
critical pressure
> ![]()
![]()
![]()
Indicate diffusion conditions (in bar and K)
> ![]()
![]()
> 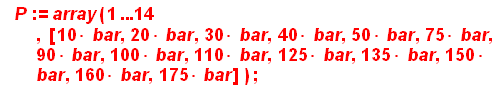
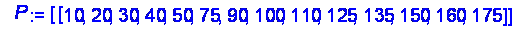
![]()
Calculate reduced temperature and pressure
> 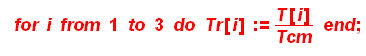
![]()
![]()
![]()
> 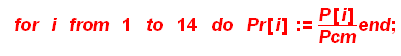
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
From here you calculate a correlating function f(Tr,Pr)
> 
![]()
> 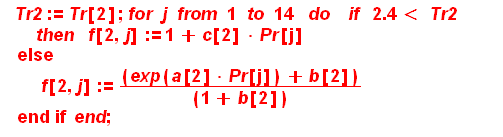
![]()
> 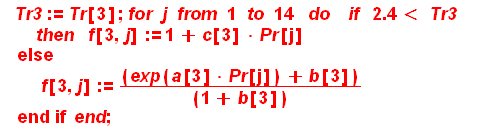
![]()
> 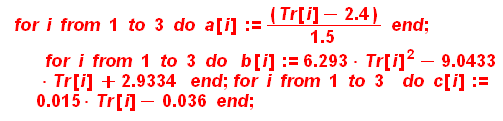
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Calculate the diffusion coefficient at conditions
> 
Plot using Matlab
> ![]()
> ![]()
> ![]()