
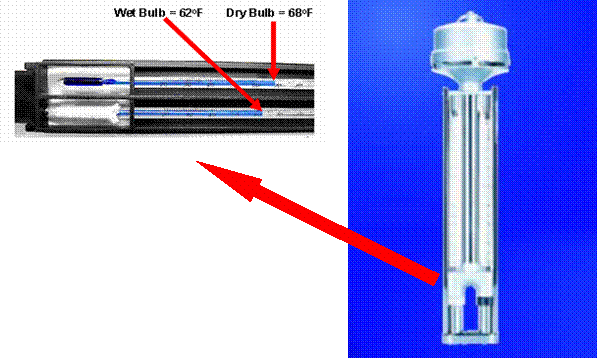
A psychrometer is an instrument commonly
used in laboratories to measure relative humidity. It is also referred to as a wet- and dry-bulb
thermometer.
This instrument consists of two similar thermometers that are
mounted side by side. The dry bulb has
its bulb exposed to the air. The wet
bulb is wrapped in an absorbent material such as muslin, which is immersed in
water and serves as a wick. When the web
bulb is taken out of the water, it cools by evaporation of the water. If the bulb is whirled around to hasten
evaporation, it is called a sling psychrometer. If air is forced past the bulb, it is
referred to as an aspirated or ventilated psychrometer.
The amount of evaporation, and consequent cooling of the
thermometer, depends on the humidity of the atmosphere—the drier the
atmosphere, the faster the water evaporates.
Using this data and humidity tables or calculations, the dew point (the
temperature to which air would have to be cooled for saturation to occur) can
be determined, and from it, the relative humidity.
Applications
Psychrometers have many applications in
commercial and industrial applications. Some of these are:
- Hospitals
- Computer rooms
- Laboratories
- Industrial plants
- Colleges and schools
- Critical storage areas
- Manufacturing plants
- Air conditioned environments
- Athletic and sport programs