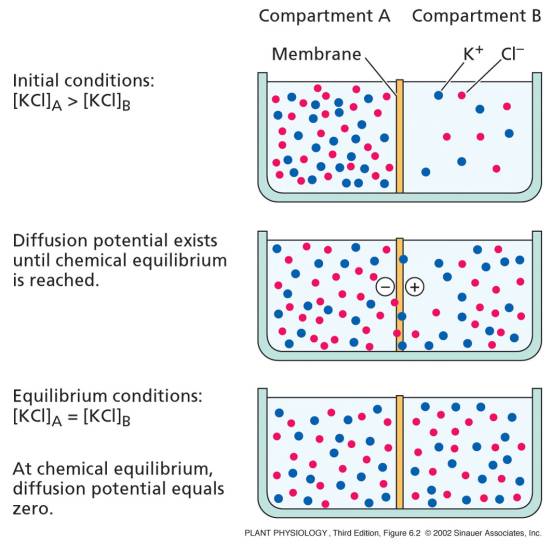
Cell membranes are the boundaries between the internal and external environments for a cell. Diffusion across this membrane is the net movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. This flow is driven by the concentration gradient. Diffusion across the membrane will continue until the concentration gradient is zero.

Figure 1: An example of diffusion with KCl across a membrane
Diffusion across cell membranes play a vital role in our world. In nature nutrients can enter the cells while wastes are allowed to leave. Synthetic membranes can be made for many uses. The smaller pores will allow only gases or water to pass, medium ones can sort out different size proteins while the larger ones may keep out micro-organisms. The knowledge obtained by studing cell diffusion can be applied in many ways. Purification and seperation processess are some of the methods that have been advanced with this knowledge.