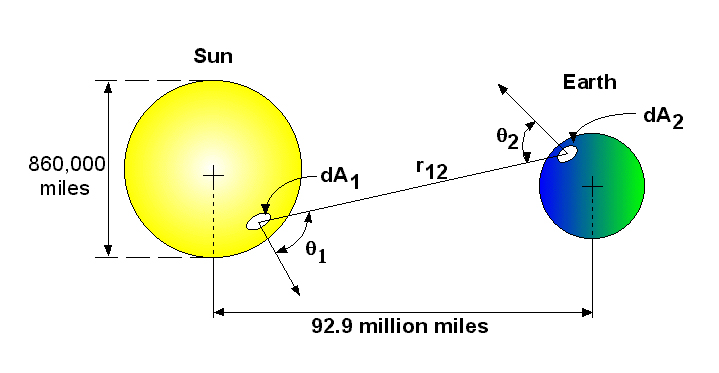
Figure 3: Sun and the Earth as Black Bodies (taken from BSL, p.444)
Example 14.4-1. Estimation of the Solar Constant
The solar constant is the radiant heat flux entering the earth's atmosphere from the sun.

> restart;
> dQ[12]:=sigma*T[1]^4*cos(theta[1])*dA[1]*dA[2]*cos(theta[2])/(Pi*r[12]^2); Eqn. 14.4-5 and in the discussion
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-11.gif)
> dSC:=dQ[12]/cos(theta[2])/dA[2];
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-12.gif)
> SC:=int(dSC/dA[1], A[1]); need to remove dA1 for Maple
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-13.gif)
> A[1]:=Pi*d[1]^2/(4*cos(theta[1])); cos(theta1) can be included because the integral(cos(theta))dA is the area of the sun, which is nearly pi*D1^2/4. For simplicity, we simply remove it after the integral has been calculated.
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-14.gif)
> SC;
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-15.gif)
> sigma:=q[b1]/T[1]^4;
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-16.gif)
> SC;
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-17.gif)
>
>
Diameter of the sun:
> d[1]:=8.60e5*miles;
![]()
Distance between dA1 and dA2:
> r[12]:=9.29e7*miles;
![]()
Heat flux:
> q[b1]:=2.0e7*Btu/hr/ft^2;
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-110.gif)
> SC;
![[Maple Math]](images/14.4-111.gif)
Which is reasonably close to the book's answer.